Feature Guide
The Satellite Tracking application features and guide information are described on this page.
If you haven't installed the application yet, click this button to take you to the store to install the app.
Download free app »

App Install Location
When the application is installed you will see it in the most-recently-used list and in the application listing dialog under 'S' - Satellite Tracking.

Future Passes 1/3
With this feature, for the satellite you are tracking and your location, you can find the dates and times the satellite is in view.
Navigate to the Menu, then select Future Passes.

Future Passes 2/3
On the page, you will see the the first station's location, name of the satellite, a radio button selector allowing you to choose
the period of time to calculate. The time periods are: 1 day, 1 week, 2 weeks, 1 month, 2 months, and 3 months.
A Start and Stop button are presented and the listing of mutual times follow.

Future Passes 3/3
A nicely formated listing of the location information, UTC date and time, azimuth, and elevation are provided for printing.

Two Station Mutual Visibility Times 1/3
With this feature, you can select a satellite and a second location (country, gird square, or specific latitude and longitude)
then perform a month's worth of calculations to see when you and the other location have mutual visibility to the satellite.
This is a handy feature for when you want to set-up a schedule with a particular station or operator. Navigate to the Menu, then select Mutual Window.

Two Station Mutual Visibility Times 2/3
On the page, you will see the the first station's location, name of the satellite, a radio button selector allowing you to choose Country, Grid Square, or specific Latitude
and Longitude. A Start and Stop button are presented and the listing of mutual times follow.

Two Station Mutual Visibility Times 3/3
A nicely formated listing of the two station's location information, mutual window times, listing index, UTC date and time, azimuth, and elevation are provided for printing.

DXCC Country Mutual Visibility 1/3
With the QTH versus DXCC Entity feature (Menu->DXCC), you can see how many DXCC entities your QTH has possible for a given satellite. A month's worth of calculations are performed across all DXCC entities and tallied up.

DXCC Country Mutual Visibility 2/3
When in the page, you can sort alpabetically or from highest elevation. Printing the results are also available. Just click the start button to beging the calculations.

DXCC Country Mutual Visibility 3/3
When you exit this page and return to the main page, you will see all the countries visible with green icons and countries which are not in red.

Can I track the planned Es'hailSat 2 now before launch?
Yes, you can. We have loaded the application with the same Keplerian elements as EUTELSAT-25B, just search for "ES'HAILSAT 2" in the search field, or select it in the Satellite's amatuer or geosynchronous list. It has catalog # 99999.

When is the planned launch of Es'hailSat-2?
Es'hailsat 2 is suppose to launch November 14, 2018.
What is the amatuer radio frequencies for Es'hailSat-2?
Narrowband Linear transponder:
2400.050 - 2400.300 MHz Uplink
10489.550 - 10489.800 MHz Downlink
Wideband digital transponder:
2401.500 - 2409.500 MHz Uplink
10491.000 - 10499.000 MHz Downlink
What are the equipment requirements for Es'hailSat-2?
X-Band 10 GHz Downlink:
– 89 cm dishes in rainy areas such as Brazil or Thailand
– 60 cm around coverage peak
– 75 cm dishes at peak -2dB
– NB: linear vertical polarization
– WB: linear horizontal polarization
S-Band 2.4 GHz NB-Uplink:
– narrow band modes like SSB, CW
– 5W nominal Uplink power (22.5 dBi antenna gain, 75cm dish)
– RHCP polarization
S-Band 2.4 GHz WB-Uplink (DATV):
– wide band modes, DVB-S2
– peak EIRP of 53 dBW (2.4m dish and 100W) required
– RHCP polarization
Can I track the Sun? Does the sun orbit the earth?
Yes, the application does show you the sun's location both in text form and on the map. We use a little trick emulating the sun does actually orbit the earth with a hand-crafted set of Keplerian elements.
See the Sun's Keplerian elements. »

Does the application do augmented reality?
Yes, the application does have augmented reality on Sky Locator page. Here you will be able to see where the satellite is located in the sky and find out if there are any
potential blocking buildings or trees. Give it a try -- we would like feedback from our users on this page. Here is a pic from the emulator - we'll add some code to get a real pic.

More augmented reality.
Here is another pic while using the application a phone tracking Es'hailsat 2 pre-launch. We have some work to do with all text on the screen :-)
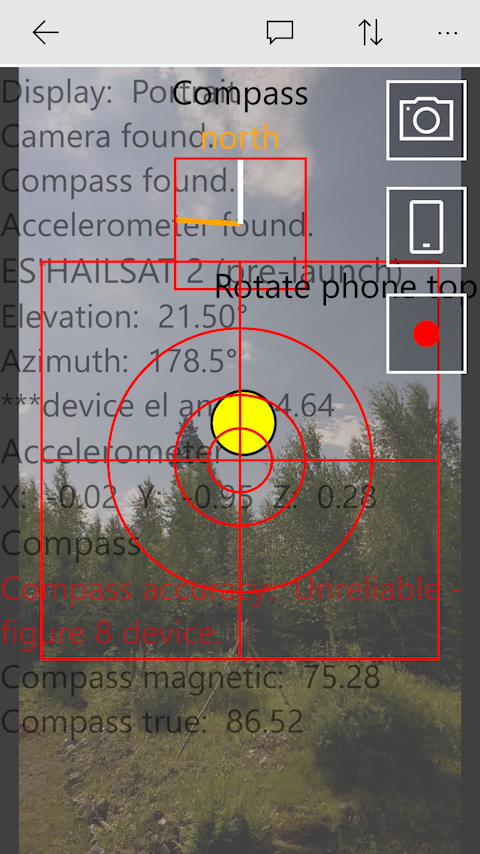
Are satellites in the atmosphere?
Yes, some satellites orbit in the outermost layer of the atmosphere called the exosphere. The exposphere layer starts at about 6,200 miles (10,000 km) above the earth which is the top of the thermosphere layer.
Molecules and atoms can escape into space from this layer. The thermopause area is located around 375 miles (600 km) above the earth just at the bottom of the exosphere layer.

What is a satellite in space?
A satellite is an ojbect in space that orbits or circles around a bigger object. There are two
kinds of satellites: artifical (man-made such as the International Space Station (ISS) or natural such as the moon orbiting the earth.
Where/what is the satellite?
A satellite is an object in space that orbits or circles around a bigger object. There are two
kinds of satellites: artifical (man-made such as the International Space Station (ISS) or natural such as the moon orbiting the earth.
How many man-made satellites are in space?
There are over 1,500 active satellites from many countries, both government and privately sponsored. There are also well over 3000 in active satellites.
Russia launched the first satellite in 1957 - this satellite was called Sputnik 1. The oldest one still orbiting was launched in 1958.

Distance between to locations supported?
Yes, on the distance page, input the latitude and longitude. This is computed to maidenhead grid square and distance. This feature can help you claim your new satellite dx record.

Convert grid to latitude and longitude?
Yes, on the distance page, input the grid square and the latitude and longitude will be calculated.

Can the map show the great circle route, maidenhead, and azimuth?
Yes, the map can show station #1's azimuth to station #2 and vice versa, plus the grid square in maindenhead coordinates. Distance is shown at mid-point.

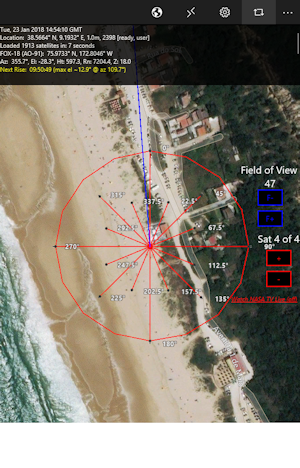
Can you show an azimuth-spider to aid in pointing my antenna? What direction do I point my dish?
Yes, the map shows an azimuth-spider overlay. The overlay is easily seen as you zoom in closer to your location. This is a great aid for antenna and dish installers.
Looks great on any device
The Satellite Tracking application looks great on any device - PC, tablet, or phone.
Download free app »
Only app you will need
The application tracks: amateur radio, brightest, communication, earth weather, geo synchronous, navigation, new, old, scientific, and space stations.
Download free app »

All in one
After selecting the satellite, calculations are displayed, you will be able to see the location details of the satellite per your location and footprint.
Download free app »

Select settings
Many options are available for map (2D 3D), location, footprint, antenna direction, and more.
Download free app »
